Plugfest

Registration
Prospective Plugfest participants must fill out the Plugfest Registration Form and email the completed form to ispcs-plugfest@iiss.at about their intention to participate. When the Plugfest Registration Form is submitted, a Plugfest Wiki account will be provided for access to the Plugfest Wiki: https://ispcs.iol.unh.edu/wiki/ where you will find further information about Plugfest.
Please note that each Plugfest participant must register for the main conference.
Planning
Plugfest participants will want to attend one of the two planning teleconferences prior to the event, where they can ask questions and make suggestions. Registered participants will be notified of the teleconferences by the Plugfest committee.
Further details about Plugfest preparation are also available on Plugfest Wiki, the login account is free to obtain when you submit the Plugfest Registration Form to ispcs-plugfest@iiss.at.
Contact
Please send comments and questions concerning the Plugfest to ispcs-plugfest@iiss.at
Plugfest Co-Chairs
- Douglas Arnold, Meinberg
- Ken Harris, Rockwell Automation
Plugfest Testing
Profiles to be tested at this year's Plugfest are:
1. Default Profile
Network topology: chain of transparent clocks (TCs) and boundary clocks (BCs). Ordinary clocks (OCs) will be included upon request. Two networks: layer-2 peer-to-peer (L2 P2P) and layer-3 end-to-end (L3 E2E).
Tests:
- Set up
- Rogue master test
- Leap second
- Connect Default networks together by BC
- Intermittent GPS availability
2. C37.238-2011
Network topology: ring of TCs. BCs hand off to TCs. OCs included upon request.
Tests:
- Set-up
- Basic interoperability, cycle through grandmasters (GMs) by changing priority 1 fields
- Rogue master test
- Injection of default profile GM
- Injection of C37.238-revision GM
- Traffic flooding tests (non-PTP traffic)
- Leap second
3. G.8265
Network topology: line of Gigabit routers/switches
Tests:
- Set-up
- Basic interoperability, GM IP addresses to be posted
- Simulation of busy networks added in series with GMs (provided by test vendors)
- Early contract termination
- Contract violation (unnegotiated Sync and Delay_Req messages)
- Leap second
4. G.8275.1
Network topology: line of BCs
Tests:
- Set-up
- Basic interoperability
- GM failover test
- Non-slave BC port test
- Rogue master test
- Injection of default profile GM
- Leap second
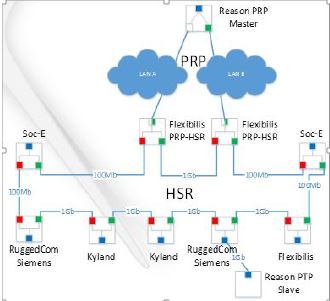
5. IEC 62439
Network topology: HSR TC ring connected to PRP network. OCs included upon request
Tests:
- Set-up
- Basic interoperability, cycle through GMs
- PRP link failure
- HSR link failure
6. C37.238 revision
Network topology: ring of TCs. BCs hand off to TCs. OCs included upon request
Tests:
- Set-up
- Basic interoperability, cycle through GMs by changing priority 1 fields
- Rogue master test
- Injection of default profile GM
- Injection of C37.238-2011 GM
- Repeat above with and without VLAN tags
- Leap second
7. IPv6 Default Profile
Network topology: line of TCs and BCs. OCs included upon request. End-to-end delay measurement.
Tests:
- Set-up
- Basic interoperability, cycle through GMs by changing priority1 fields
- Cycle through address scope settings
8. New Technology
New technology/profiles will be set up based on availability of multi-organization implementations. Possible networks include:
- Enterprise Profile
- SMPTE Profile
- IEEE 802.1AS
- White Rabbit
- Experimental implementations of IEEE 1588 revision features